Difference between revisions of "DiffEqs"
From Sean_Carver
(→Bilayer Membrane with Na/K Pumps) |
|||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
<math> C \frac{dV(t)}{dt} = I(t) </math> | <math> C \frac{dV(t)}{dt} = I(t) </math> | ||
| − | <math> V(0) = - | + | <math> V(0) = -75 </math> |
== Bilayer Membrane with Na/K Pumps and Leak Channels == | == Bilayer Membrane with Na/K Pumps and Leak Channels == | ||
== Bilayer Membrane with Na/K Pump, Leak & HH Channels == | == Bilayer Membrane with Na/K Pump, Leak & HH Channels == | ||
Revision as of 15:20, 8 February 2009
Contents
Plain Bilayer Membrane
A plain lipid bilayer is approximately an ideal capacitor. The equation for an ideal capacitor is
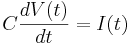
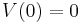
Here C is a constant (parameter), the capacitance of the membrane, proportional to area.
Next V(t) is the membrane potential. This is the quantity of interest.
Next I(t) is the injected current into the cell.
Finally V(0) is the initial membrane potential of the cell.
Bilayer Membrane with Na/K Pumps
Same, except that the initial condition is different.